Air Quality Life Index 2024
Introduction
The Air Quality Life Index 2024 was just produced by the University of Chicago’s Energy Policy Institute (EPIC). In India, about 40% of the population breathes air over the yearly PM2.5 threshold of 40 µg/m³.
What is the Air Quality Life Index?
- The AQLI is a pollution indicator that calculates how much longer life expectancy is impacted by particulate air pollution.
- The true cost of particle pollution in communities worldwide is then determined by combining the association between long-term human exposure to air pollution and life expectancy with the Index.
- The Index also shows how measures reducing air pollution can lengthen life expectancy when they adhere to current national air quality regulations, user-defined air quality thresholds, or WHO guidelines for acceptable exposure levels.
What are the Key Findings of the Air Quality Life Index 2024?
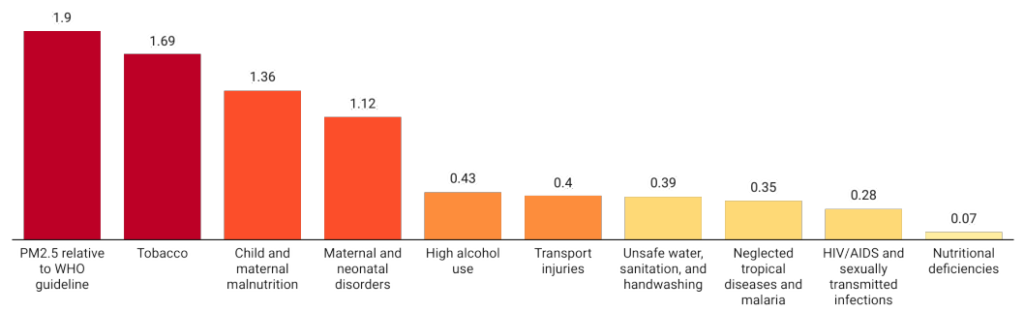
- Impact of Air Pollution on Life Expectancy: Concurring to the examination, the normal person’s life anticipation might increment by 1.9 a long time, including 14.9 billion lives a long time worldwide add up to, if PM2.5 (particulate matter with a distance across of 2.5 µm or less) contamination were diminished to meet WHO limits.
- Deadlier than Chronic Diseases: Air pollution has consequences that are larger than those of smoking, binge drinking, and other major health concerns including HIV/AIDS and malnutrition by a factor of several.
- Uneven Distribution of Pollution: Individuals who live in the most polluted locations typically have a 2.7-year shorter life expectancy because they breathe six times as much dirty air as people who live in the cleanest places.
- Non-Compliance: Despite many nations having set national air quality guidelines, the report shows that compliance and enforcement continue to be very difficult. 37 of the 94 countries that have set PM 2.5 standards, according to the research, do not comply with their regulations. Furthermore, 158 nations have not established any guidelines at all.
- Potential Benefits: Meeting WHO pollution criteria has significant potential advantages. The average life expectancy in these regions would increase by 1.2 years if all countries met their targets.
- Global Scenario
- US, China, Europe
- Stricter regulations have been enacted in the US, Europe, and China, which has resulted in notable drops in pollution levels.
- Since 2014, China has seen a 41% reduction in air pollution and a 2-year increase in the average lifespan of its citizens.
- Since 1970, the US has cut pollution by 67.2%, which has increased the average lifespan by 1.5 years.
- In Europe, life expectancy has increased by 5.6 months due to a 30.2% decrease from 1998.
- South and Southeast Asia
- Significant progress was observed in South and Southeast Asia in 2022, with a 4% decrease in PM2.5 levels from 2012 to 2022.
- Even with this progress, South Asia continues to be the most polluted region in the world, contributing 45% of the years that people lose to excessive pollution worldwide.
- Pakistan, Bangladesh, India, and Nepal are some of the world’s most polluted nations.
- Air pollution in Myanmar is taking 2.9 years off people’s life expectancy.
- Africa
- In 2022, air pollution in Central and West Africa has not significantly changed.
- The average concentration of PM2.5 in the area is 22.2 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m3), which is 4.4 times higher than the WHO recommendation.
- In the locale, this level of contamination is causing life anticipation to drop by a normal of 1.7 a long time.
- Nonetheless, norms and regulations for air quality have recently been put into place in Ghana, Rwanda, and Nigeria.
- West Asia
- The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region has become a new hotspot for pollution, with an average 1.3-year drop in life expectancy.
- The two most polluting nations in the area are Iraq and Qatar.
- Latin America
- The PM2.5 levels in Latin America rose by 3.8% from 1998 and 4.8% from 2021.
- The most polluted nation in Latin America is Bolivia; in Guatemala, air pollution shortens life expectancy by 2.1 years.
- To reduce pollution, cities like Quito, Bogotá, and Mexico City enhance public transportation and impose driving limits.
- US, China, Europe
What are India Specific Findings of the Air Quality Life Index 2024?
- Impact of Cleaner Air on Life Expectancy in Delhi
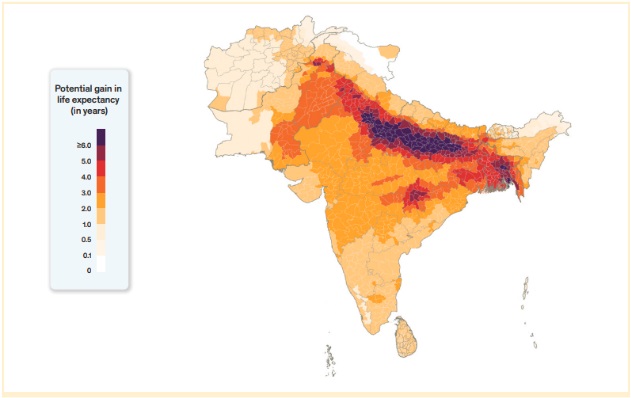
- The 18.7 million people who live in Delhi may live an additional 7.8 years longer if the air quality meets WHO limits of 5 µg/m³.
- Reaching 40 µg/m³, India’s national air quality threshold might add 4.3 years to life expectancy.
- Current Air Quality and Trends in Delhi
- Delhi has the highest average PM2.5 level (84.3 µg/m³) of any Indian city in 2022.
- Nonetheless, Delhi has significantly improved, with an average annual PM2.5 concentration of 84.3 µg/m3 in 2022.
- Improvement in Air Quality Across India
- Particulate pollution in India decreased from 49 µg/m³ on average during the previous ten years to 41.4 µg/m³ in 2022.
- The ordinary Indian could live nine months longer if this decline in pollution persists than if they were subjected to the levels seen in the prior ten years.
- Comparison with Other Health Risks
- An inhabitant of India loses 3.6 years of life due to particulate pollution, 1.6 years due to malnourishment, 1.5 years due to tobacco use, and 8.4 months due to unsanitary and hazardous water sources.
How Can We Control Air Pollution?
- Prevention
- Reduce, remove, or avoid pollution at its source by implementing pollution prevention strategies.
- A few cases incorporate utilizing less hurtful fills or crude materials, utilizing less contaminating mechanical forms, and expanding handle effectiveness. For instance, the BSVI engine.
- Adoption of Clean Air Technology
- Technologies for preventing and regulating air pollution can aid in the reduction of air pollution.
- Biological degradation, condensers, absorbers, adsorbers, fabric filters (baghouses), electrostatic precipitators, and wet scrubbers are some of its components.
- Economic Incentives: Financial incentives, such as emissions trading and caps, may be employed by sectors that produce pollution.
- Scrapping Old Vehicles: Reducing the nation’s End-of-Life Vehicle (ELV) fleet will result in a 15-20% decrease in emissions related to traffic pollution.
- Work-from-Home: The government may encourage work-from-home regulations on days with high pollution levels, such as winters, to reduce air pollution.
- Artificial Rain: It can remove airborne contaminants suspended in the atmosphere, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM).
- Behavioral Change: Encouraging walking, bicycling, and public transportation can reduce the number of private vehicles on the road, reducing air pollution and emissions.
What are the Government Initiatives Taken for Controlling Air Pollution?
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) Portal
- Air Quality Index
- Graded Response Action Plan (for Delhi)
- New Commission for Air Quality Management
- National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP)
Conclusion
The Air Quality Life Index 2024 underscores a critical need for global action on air pollution. With 40% of India’s population exposed to hazardous PM2.5 levels, the index reveals stark realities: potential gains of up to 1.9 years in life expectancy if WHO guidelines are met, contrasting with non-compliance in many nations. Stricter regulations in regions like the US, China, and Europe offer hope, but urgent, coordinated efforts are essential to safeguard public health worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Which is the most polluted city in India in 2024?
Byrnihat, which is near the border between Assam and Meghalaya, was named the most polluted city in India in H1 2024 with an average PM2.5 concentration of 140 µg/m³.
Why is AQI so high in India?
The largest contributor to air pollution in India is waste burning, at 59%, followed by dust and construction. While waste burning occurs predominantly in rural regions (agricultural), crafting is primarily done in urban areas.
Where is air pollution the worst in 2024?
Top 10 Most Polluted Cities in the World (2024)
1) Osorno, Chile.
2) Et Tira, Israel.
3) Ashton, New Zealand.
4) Bhagalpur, India.
5) Cuernavaca, Mexico.
6) Nuneaton, United Kingdom.
7) Abu Qir, Egypt.
8) Diadema, Brazil.Which city is the cleanest in India by AQI?
List of Cities with Best Air Quality in India (2024)
Aizawl (9.9 μg/m3)
Gangtok (14.8 μg/m3)
Chamarajanagar (17.7 μg/m3)
Gadag (18 μg/m3)
Chikkamagaluru (18.2 μg/m3)
Madikeri (19 μg/m3)
Thiruvananthapuram (19.1 μg/m3)
Koppal (19.2 μg/m3)
Sources:
- https://www.indiatoday.in/india/delhi/story/delhi-life-expectancy-reduction-12-years-due-air-pollution-air-quality-life-index-report-2589631-2024-08-28
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/india-saw-193-drop-in-particulate-pollution-in-2022-adding-51-days-to-life-expectancy-aqli/article68575637.ece
- https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/delhi-residents-lose-nearly-12-years-of-their-lives-to-air-pollution-report-6438842
- https://epic.uchicago.edu/area-of-focus/aqli/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Air_quality_index
- https://www.worldeconomics.com/Indicator-Data/ESG/Environment/Air-Quality/
- https://www.timesnownews.com/health/delhis-air-pollution-may-reduce-life-expectancy-of-residents-by-12-years-warns-report-know-how-article-112884271
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/world-news/no-country-meets-who-air-quality-standard-life-span-cut-by-2-3-years-globally-report-finds-101693358888894.html

Leave a Reply