Bharat 6G Vision: Empowering India’s Digital Decade
Introduction
During the “Bharat 6G 2025” International Conference, India reaffirmed its resolve to spearhead the global race in 6G technology, underlining 6G as a revolutionary possibility at the scale of civilization and in line with the Bharat 6G Vision.
What is Bharat 6G Vision?
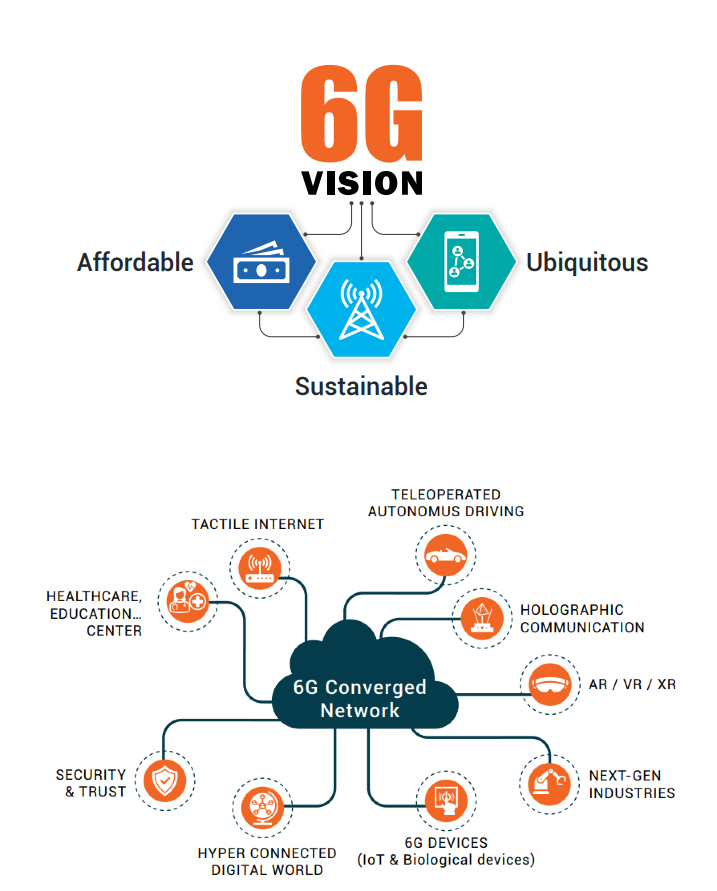
The objectives of the Bharat 6G Vision, which was introduced in 2023, are affordability, sustainability, and ubiquity. The goal is for India to become a world leader in sixth-generation (6G) telecoms by 2030.
What is the Objectives of Bharat 6G Vision?
- Establishing a robust 6G research ecosystem
- Encouraging indigenous 6G innovations
- Enhancing digital connectivity for rural and urban regions
- Promoting sustainability in 6G network development
- Strengthening India’s position in global 6G standards
What is Significance of Bharat 6G Vision?
- Economic Growth and Digital Transformation
- Boost to GDP: By 2035, 6G is expected to generate $1 trillion for India’s economy, transforming both established and emerging businesses.
- Indigenous Innovation and Manufacturing: The goal is to promote self-reliance (“Atmanirbhar Bharat”) in the telecom industry by giving priority to the design, development, and deployment of 6G technologies in India. This include helping entrepreneurs, fostering R&D, and encouraging the production of 6G components domestically.
- Job Creation: Being at the forefront of 6G technology will lead to a large increase in employment in the manufacturing, service, research, and development industries.
- Bridging the Digital Divide and Enhancing Quality of Life
- Ubiquitous Connectivity: 6G seeks to close the digital divide and connect underserved communities by offering inexpensive, very fast, and secure connection in both urban and rural locations.
- Transforming Key Sectors:
- Healthcare: Enabling advanced telemedicine, robotic surgeries, and AI-based diagnostics, with potential for “Hospital-to-Home” services.
- Agriculture: Facilitating smart monitoring and precision farming using IoT sensors and AI/ML for optimized yields and resource management.
- Education: Enabling real-time immersive learning through AR/VR technologies and access to high-quality educational resources.
- Industrial Automation: Powering Industry 4.0 with enhanced machine-to-machine communication, digital twins, and IoT for smart industries and remote-controlled factories.
- Transportation: Supporting urban air mobility (UAM), autonomous vehicles, and intelligent traffic management.
- Global Leadership and Strategic Importance
- Influencing Global Standards: India wants to actively participate in organizations such as the worldwide Telecommunication Union (ITU) in order to influence and contribute to worldwide 6G standards. Ensuring interoperability and a worldwide reach for India’s breakthroughs is imperative.
- Strategic Partnerships: In addition to strengthening research and development and ensuring robust supply chains, the Bharat 6G Vision promotes partnerships with prominent international 6G alliances, such as the USA’s NextG Alliance, Europe’s 6G-IA, and Japan’s XG Mobile Promotion Forum.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Creation: India wants to establish itself as a pioneer in the development of next-generation telecoms by making a substantial contribution to the global 6G network.
- Geopolitical Influence: India’s position as a world leader in providing cutting-edge and reasonably priced telecom solutions enhances its reputation internationally and fosters digital transformation for the good of all people.
What is the Features of the Bharat 6G Vision?
- Technology and Performance
- Ultra-High Data Rates: Aims for rates far faster than 5G, maybe as high as 1 Terabit per second (Tbps), which would allow for ultra-fast data processing and immersive experiences in real time.
- Ultra-Low Latency: For time-sensitive applications like remote surgery, industrial automation, and driverless cars, aiming for latency as low as 1 microsecond is essential.
- Ubiquitous Connectivity: Envisions integrated land, sea, and space communication, including the integration of satellites and other terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks (NTN) for all-encompassing coverage, particularly in underserved and rural regions.
- Massive Device Connectivity (IoT): Facilitates the expansion of the Internet of Everything (IoE) by supporting the connecting of billions of devices, opening the door for smart industries, smart cities, and smart agriculture.
- AI-Powered Networks: Incorporates machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) for effective resource management, predictive maintenance, network optimization, and customized user experiences.
- High-Frequency Bands: Investigates using higher frequency bands to increase bandwidth and capacity, such as the millimeter-wave (mmWave) and terahertz (THz) spectrum.
- Advanced Features: Will make it possible for cutting-edge applications including immersive Extended Reality (XR) experiences, digital twins, holograms, and multisensory communications.
- Strategic Pillars and Goals
- Affordability: Prevents a digital gap by guaranteeing that 6G services and technologies are available and reasonably priced for all residents.
- Sustainability: Focuses on creating environmentally friendly solutions and energy-efficient networks in order to reduce the carbon impact.
- Ubiquity: Strives for smooth connection and broad availability throughout the country.
- Indigenous Innovation: Supports the creation, development, and production of 6G solutions in India in line with the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (Self-Reliant India) program.
- Global Leadership: Establishes India as a major provider of cutting-edge and reasonably priced telecom products and a major contributor to the development of global 6G standards.
- Security and Privacy: Places a high priority on strong security mechanisms, like as authentication and encryption, to safeguard private information in a networked world.
- Implementation Approach
- Phased Roadmap: A well-defined plan (e.g., Phase 1: R&D and proof-of-concept, 2023-2025; Phase 2: commercialization and statewide deployment, 2025-2030).
- Collaborative Ecosystem: Creates the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA), a nationwide forum for cooperation between government agencies, businesses, research institutes, and entrepreneurs.
- Testbeds and Labs: Focuses on assisting academic labs for research and capacity growth, as well as establishing cutting-edge 6G testbeds, such as the 6G Terahertz Testbed.
- IPR Creation: Focuses on developing 6G technologies’ intellectual property rights (IPR), with India actively participating in international patents.
- International Partnerships: Builds partnerships with worldwide 6G forums and groups to promote knowledge exchange and conform to global standards.
- Application-Centric Development: Drives the creation of 6G application cases in a number of industries, including transportation, industrial automation, healthcare, and agriculture.
What are the Challenges in Bharat 6G Vision Implementation?
Despite its promising prospects, Bharat 6G Vision faces several challenges:
- Research & Development (R&D) and Technological Hurdles
- Fundamental Research: Globally, 6G research and development is still in its infancy. Terahertz (THz) communication, AI/ML integration in networks, quantum communication, enhanced antenna designs (such as massive MIMO for THz), and novel network architectures are only a few of the core research fields in which India has to make significant investments.
- High Frequencies: Using higher frequency bands (mmWave and THz) requires creative beamforming techniques and dense network installations due to signal propagation issues (shorter range, sensitivity to obstructions).
- Infrastructure and Deployment Challenges
- Massive Infrastructure Investment: Massive financial investments in fiber optic networks, tiny cells, and base stations will be necessary to upgrade current telecom infrastructure and roll out new, dense 6G networks, especially in rural and isolated locations.
- Fibre Connectivity: Fiber connectivity is currently lacking in a substantial percentage of India’s telecom towers, which is necessary for backhauling the enormous amounts of data traffic that 6G would create. One essential precondition is rapid fiberization.
- Funding and Economic Viability
- High Costs: The cost of creating and implementing 6G technology is quite high. It will be crucial to get sufficient and ongoing support from both public and private sources.
- Revenue Sharing: Telecom operators and Over-The-Top (OTT) service providers are engaged in continuing discussions over revenue sharing. The operators want a reasonable portion of income to support their infrastructure developments.
- Spectrum Management and Regulatory Framework
- pectrum Availability and Allocation: The work of finding and assigning new, higher-frequency spectrum bands for 6G is challenging because it must balance the demands of several stakeholders, including telecom carriers, the military, space, etc. Global spectrum harmonization is also essential.
- Policy Adaptations: The legislative structure must change quickly to meet the special demands of 6G, which include dynamic spectrum sharing, security, and privacy concerns.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy
- Enhanced Threats: 6G networks may be more vulnerable to advanced cyberthreats and vulnerabilities because to their extremely high speeds, enormous data volumes, and hyper-connectivity. Strong security protocols, such as cutting-edge encryption and threat detection powered by AI, will be essential.
- Data Privacy: It will be very difficult to maintain strict data privacy and compliance with changing legislation as a result of the explosion of data and the integration of AI.
Conclusion
Bharat 6G Vision is set to revolutionize India’s digital landscape, ensuring that the nation remains at the forefront of technological advancements. By fostering innovation, infrastructure development, and global collaborations, Bharat 6G Vision will shape the future of connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the Bharat 6G Vision?
India’s ambitious aim to dominate the world in 6G technology by 2030 is known as the Bharat 6G Vision. It was introduced by the Prime Minister in March 2023 with the goal of promoting domestic 6G solution design, development, and deployment, establishing India as a major player in the future of international telecommunications.
How will Bharat 6G contribute to India’s economy?
It is projected that 6G would significantly increase India’s economic might. By 2035, it is anticipated to boost India’s GDP by $1 trillion through the development of new industries, the transformation of already-existing sectors (manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture), the encouragement of domestic innovation, and the creation of significant job opportunities.
What is the role of the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA)?
An important venue for collaboration that unites Indian business, academia, research institutes, startups, and government agencies is the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA). Its main responsibilities are to promote innovation, advance R&D, ease standardization, and establish global alliances in order to realize the objectives of the Bharat 6G Vision.
How will Bharat 6G impact everyday life in India?
1.“Hospital-to-Home” services and sophisticated telemedicine.
2. AI-driven insights for farmers in smart agriculture.
3. Immersive learning environments using AR and VR.
4. Autonomous vehicles and smart cities that are efficient.
5. Multisensory interactions and real-time holographic communication.
6. Closing the digital divide even further, particularly in rural regions.
Sources:
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2118200
- https://byjus.com/free-ias-prep/air-spotlight-bharat-6g-vision-telecom-technology-to-empower-people/
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/pm-modi-unveils-indias-6g-vision-document-says-initiative-shows-indias-confidence-nation-becoming-big-telecom-tech-exporter/article66649229.ece
- https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/telecom/bharat-6g-alliance-forms-key-strategic-european-partnerships-to-drive-innovation-12753121.html
- https://informatics.nic.in/files/websites/january-2025/bharat-6g-alliance-joins-global-forces-to-shape-the-future-of-telecom.php
- https://www.meity.gov.in/static/uploads/2024/12/10fcadec462c330211502fed3d24ea83.pdf
- https://www.ril.com/ar2022-23/digital.html
Leave a Reply