Burqa Ban in Switzerland, 2025
Introduction
Starting on January 1, 2025, Switzerland has banned face-covering clothing, such as niqab and burqa. This legislation, which was adopted by a national vote in March 2021, is a reflection of the continuing global discussion about the wearing of burqas and hijabs, which has also generated a lot of discussion in India.
What are the Highlights of the Burqa Ban by Switzerland?
- Scope and Penalties: In public areas and private structures that are open to the public, it is illegal to hide one’s mouth, nose, or eyes. A fine of up to 1,000 Swiss francs will be imposed for breaking the restriction.
- Exceptions: Planes, diplomatic buildings, houses of religion, health and safety issues, local traditions, weather, creative endeavors, and personal protection with prior authorization are among the exceptions to the prohibition.
Which Countries Have Banned Face Veils(Niqab and Burqa)?
- France: In 2011, it became the first European nation to outlaw full-face veils in public, after religious symbols in schools were restricted since 2004.
- China: In Xinjiang province, it outlawed long beards, veils, and burqas in 2017 as part of its anti-extremism policies.
- Belgium: When full-face veils were outlawed in 2011, offenders faced fines or perhaps up to seven days in prison. The European Court of Human Rights upheld the prohibition in 2017.
- Sri Lanka: After a temporary ban following the 2019 Easter bombings, Turkey permanently outlawed face coverings in 2021, claiming national security.
- Tajikistan: Even though more than 95% of people are Muslims, hijabs for women were formally outlawed in 2024.
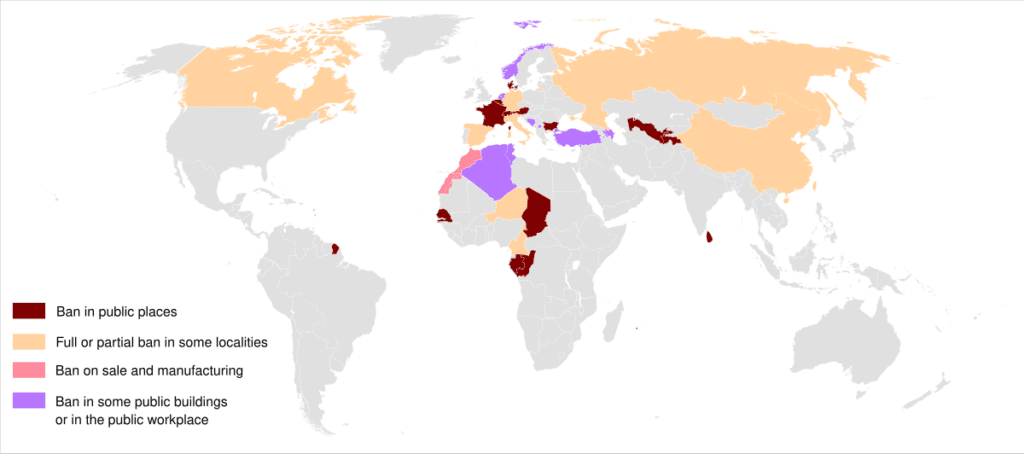
With differing degrees of limitations, the hijab is also prohibited in Germany, Australia, Austria, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Canada, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Uzbekistan.
What is the Status of Niqab and Burqa in India?
- Amna Bint Basheer v CBSE, 2016
- In Amna Bint Basheer v. CBSE, 2016, the Kerala High Court maintained the CBSE clothing regulation while ruling that the hijab is a necessary religious practice, permitting further protections and procedures similar to those in 2015.
- The clothing code, according to the Central Board of School Education (CBSE), was implemented to discourage unfair behaviors.
- Kerala High Court, 2018
- Two girls sought to wear a headscarf, but the Christian missionary school forbade them from doing so in the 2019 case of Fathima Thasneem v. State of Kerala.
- The school’s “collective rights” must supersede the rights of individual students, the court said, upholding the school’s decision.
- Resham v. State of Karnataka, 2022
- The state government’s prohibition on hijabs at government colleges was upheld by the Karnataka High Court in March 2022.
- The HC maintained the prohibition, ruling that it did not infringe upon the right to free speech and expression and that donning a hijab did not constitute an important religious practice.
- Split Verdict by Supreme Court (SC), 2022
- The two-judge SC bench in Resham v. State of Karnataka, 2022, rendered a divided decision. The matter has now been sent to a bigger SC bench.

What are the Arguments in Favour and Against Such Ban of Burqua?
Arguments in Favour of Ban
- Uniformity and Discipline: Establishing a dress code encourages discipline and consistency in school settings. It keeps a space free from religious divides and neutral by prohibiting the exhibition of overt religious symbols.
- Gender Equality: The hijab and related customs are frequently seen as patriarchal instruments that limit women’s independence and maintain gender inequity.
- Integration into Society: By outlawing such behaviors, we may prevent the potential alienation brought on by overt religious symbols and promote assimilation into society at large.
- Not Absolute Fundamental Right: Reasonable limitations may be placed on fundamental rights, which are not unqualified. Particularly at government-funded educational institutions, the right to religion guaranteed by Article 25 cannot supersede other basic rights.
- Security Concerns: These prohibitions also seek to improve public safety in high-risk regions, discourage the abuse of clothing to conceal weapons, and prevent anonymity that might impede identification.
Arguments Against Ban
- Freedom of Religion: The freedom to exercise and profess one’s religion is protected by Article 25 of the Indian Constitution; prohibiting such activities might increase societal tensions and foster alienation.
- Autonomy and Choice: Enforcing a prohibition violates people’s right to personal freedom and their ability to choose their own clothes, especially women.
- Impact on Education: Restricting the hijab may deter conservative female students from going to school, which would be detrimental to their education and sense of empowerment.
Conclusion
The discussion over the hijab and burqa emphasizes the necessity of striking a balance between institutional discipline, social ideals, and individual liberties. Although the Constitution guarantees religious freedom, this protection is not unqualified and must be in line with equality and public order. Court decisions place a strong emphasis on gender equality and inclusion, highlighting the value of promoting discussion and developing laws that uphold individual liberties without limiting educational opportunities or excluding populations.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Which European country banned the burqa first?
France government imposed a stringent prohibition on religious signs in government buildings and public institutions, claiming that they were against secular rules. France outlawed the burqa, a full-body covering that conceals the face, and other headwear that covers the face in public places in 2011.
Why are burqas being banned?
The counter-jihad movement has been connected to campaigns to outlaw the burka. As Dutch politician Geert Wilders suggested banning hijabs, Islamic schools, new mosques, and non-Western immigration, such proposals may be connected to other relevant cultural bans.
When Karnataka Government Ban Hijab?
The Karnataka government issued a directive in 2022 that forbade the hijab, or headscarf, to be worn in government schools.
How many countries have banned the burqa?
The burqa (hijab) is now prohibited in 16 countries, including China (in the Xinjiang Region), Morocco, Switzerland, Austria, Denmark, France, Belgium, Tajikistan, Bulgaria, Cameroon, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Gabon, and the Netherlands.
Sources:
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/swiss-burqa-ban-to-take-effect-from-2025/article68836263.ece
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/swiss-burqa-ban-9755000/
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/world-news/swiss-burqa-ban-to-take-effect-from-january-1-what-are-the-exceptions-101731037833556.html
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-56314173
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/europe/swiss-parliament-approves-ban-on-burqas-sets-fine-for-violators/articleshow/103824210.cms

Leave a Reply