India-Afghanistan Relations, 2025
Introduction
Driven by pragmatic engagement between New Delhi and the Taliban regime amid altering regional dynamics, security concerns, and a renewed economic cooperation, India-Afghanistan ties have entered a significant new phase in 2025. This article analyzes recent trends, economic linkages, security concerns, human connectivity, and the wide-ranging ramifications for both countries in order to provide a distinctive, thorough, and SEO-optimized summary of these ties.
What Recent Activities Have Affected India-Afghanistan Relations?
- Direct Diplomatic Engagement with the Taliban-led Government
- Afghan Acting Foreign Minister Amir Khan Muttaqi’s visit signaled warmer relations and improved communication since it was the country’s first direct diplomatic encounter with the Taliban-led administration since 2021.
- Muttaqi’s visit was made possible by the lifting of travel restrictions by the UN Security Council’s Sanctions Committee, demonstrating international diplomatic accommodation.
- Upgrade of Indian Mission in Kabul
- India and Afghanistan reached an agreement to swap diplomats, allowing for ongoing diplomatic interaction.
- India’s intention to expand its diplomatic presence and take formal recognition measures is demonstrated by its move from a technical mission to a full-fledged embassy.
- Commitments on Sovereignty and Security
- Both countries reaffirmed their respect for territorial integrity and sovereignty, with Afghanistan making the vital security pledge to forbid the use of its territory against India.
- Enhanced Trade Relations
- Despite political unpredictability, both administrations are dedicated to increasing bilateral commerce in an effort to revitalize economic relations.
- The opening of the India-Afghanistan Air Freight Corridor, which would increase direct trade and business between the two nations, was hailed by all parties.
- Humanitarian and Development Initiatives
- Soft power and developmental diplomacy were demonstrated by India’s announcement of infrastructural initiatives, such as the building of a hospital and increased humanitarian assistance.
- India stated that it would be willing to help the Afghan government rebuild homes in places damaged by earthquakes.
Why Are India-Afghanistan Relations Important?
- Strategic Geopolitical Partnership
- India views Afghanistan as essential to maintaining regional stability and thwarting hostile influence, especially that of Pakistan.
- India’s strategic decision to engage the Taliban as a counterbalance to Pakistan’s regional influence was driven by the deterioration in Afghan-Pakistan ties.
- A long-term strategic commitment is demonstrated by India’s assistance to the Northern Alliance in the 1990s and its position as one of Afghanistan’s biggest regional development partners.
- Counterterrorism Collaboration
- India aggressively worked to strengthen Afghan security forces’ capabilities after 2001 in an effort to keep Afghanistan from turning into a hub for terrorism.
- As the world changes, counterterrorism cooperation is developing, as seen by the Taliban-led Afghan government’s recent commitment to forbid the use of Afghan territory against India.
- Development and Reconstruction Contributions
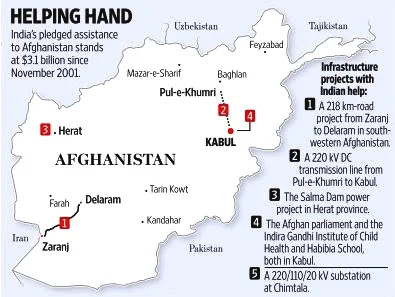
- India’s commitment to Afghan development as a form of soft power is demonstrated by its significant investments in infrastructure projects, including the Salma Dam, the Zaranj-Delaram highway (a major trade route that avoids Pakistan), Kabul’s parliament building, hospitals, and power substations.
- Initiatives like COVID-19 and drought relief are prime examples of India’s dedication to Afghan development.
- Economic and Trade Connectivity
- Given Afghanistan’s $1–3 trillion mineral riches, India sees potential for commerce and mining as a source of income.
- Allows India to circumvent Pakistan and promote commerce by taking part in regional conferences and infrastructure projects like the Chabahar Port (Iran-Afghanistan-India corridor).
- Deep Rooted Cultural Bonds
- As shown by their common languages, faiths, and cultural exchanges, India and Afghanistan have long-standing historical, cultural, and civilizational relations.
- Bollywood’s popularity in Afghanistan and Indian scholarships for Afghan students reflect continuing cultural diplomacy.
- Diplomatic Engagement Amid Political Shifts
- India’s recent diplomatic approach to Taliban-led Afghanistan, which included receiving Taliban officials and promoting its Kabul mission to full embassy status, exemplifies practical diplomacy that strikes a balance between ground realities and reluctance to acknowledge.
- Pakistan’s disruptive actions and China’s expanding Central Asian influence are balanced by India-Afghanistan relations. India’s role in fostering political cooperation and regional connectivity is further reinforced by its involvement in regional forums such as the Heart of Asia-Istanbul Process.
What are the Major Challenges Facing India-Afghanistan Relations?
- Security Concerns and Terrorism
- Even with diplomatic efforts, terrorism is still a serious problem.
- Because of the Taliban’s longstanding ties to terrorist organizations like Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed, there are concerns that Afghanistan might become a safe haven for terrorists opposed to India.
- Despite the Taliban’s 2025 promise to forbid the use of Afghan territory against India, doubts remain because of their partial disengagement from terrorist organizations.
- Pakistan’s Influence and Proxy Dynamics
- Afghanistan is where Pakistan and India’s strategic competition is most evident.
- Peace and security have been made more difficult by Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), which has consistently aided the Taliban and its proxies.
- Although Afghan-Pakistan relations have worsened as a result of the Taliban’s unwillingness to suppress Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), who carry out insurgency in Pakistan, there is still a chance of cross-border instability.
- Political Instability and Governance Issues
- The Taliban’s non-democratic rule runs counter to India’s advocacy of an inclusive political process headed by Afghans.
- India’s values-based involvement is undermined by the suppression of dissent, the lack of protections for minorities, and the lack of women’s rights.
- The debate over the exclusion of female journalists from Taliban-led news conferences in India in 2025 serves as an example of the challenges of working with a government that has a dismal human rights record.
- Economic and Infrastructure Challenges
- Afghanistan is still among the poorest nations in the world.
- India’s numerous investment projects, including the Kabul parliament and the Salma Dam, are hampered by security concerns.
- Trade and project continuity are hampered by the Taliban’s rule and international sanctions. Nonetheless, India’s encouragement of commerce through the Chabahar port and invitations to the mining industry point to cautious hope.
- Growing Chinese Influence
- India faces a geopolitical threat from China’s growing influence in Afghanistan, which includes investments in infrastructure and discussions with the Taliban.
- India faces a strategic dilemma as the China-Afghanistan-BRI nexus develops since it may strengthen Beijing’s hold on important resource corridors and regional connections, reducing India’s influence in South Asian geopolitics.
- Drug Trafficking and Narcotics
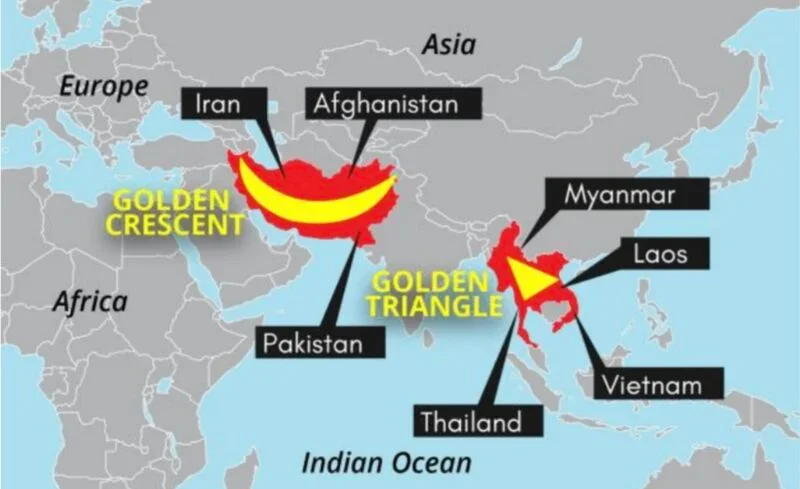
- The Golden Crescent, which consists of Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, is centered on Afghanistan, the world’s largest producer of opium, which contributes to regional instability.
- The drug trade finances terrorist activities and damages India, particularly areas like Punjab that are experiencing drug addiction crises.
- Drug trafficking from the Golden Crescent is still a top issue for cross-border security, which makes bilateral relations more difficult.
What Strategic Steps Should India Take to Strengthen India-Afghanistan Relations?
- Sustain Diplomatic Engagement while Withholding Full Recognition
- India elevated its technical mission to a full embassy in Kabul in 2025 after adopting the practical “engage but not recognize” policy in 2021 following the Taliban takeover.
- Without instant political recognition, India should keep up and expand its formal channels (full embassy, frequent diplomatic contacts).
- By continuing its limited involvement and offering humanitarian assistance instead of official recognition, India should show that moral obligation should not be subordinated to strategic need, making sure that its actions are both sensible and morally just.
- Expand Targeted Development & Humanitarian Diplomacy
- By increasing infrastructure collaboration, diplomatic engagement, and capacity-building aid, India should continue to oppose the growing Chinese influence while upholding strategic autonomy, a notion emphasized in its foreign policy theories such as “Act East” and “Neighbourhood First.”
- In order to foster goodwill and stabilize communities, India should keep up its visible, needs-based projects in the areas of health, water, education, and reconstruction.
- India is restarting and growing a number of infrastructure and healthcare initiatives, including the building of a Thalassemia Center, five maternity clinics in provinces including Paktika and Khost, an oncology and trauma center, and a 30-bed hospital in Kabul’s Bagrami district.
- Through development diplomacy—a strategy exemplified by Japan’s assistance to Southeast Asia—these programs stabilize local communities, cultivate goodwill, and increase soft power.
- Strengthen Counter-terrorism Cooperation
- Establish, within the bounds of the law, real-time intelligence sharing, cooperative investigations, and capacity building for Afghan security forces.
- Boost demand-reduction initiatives, interdiction, and cross-border anti-narcotics cooperation in the Golden Crescent’s source and transit regions.
- India should keep funding Afghan security capacity-building initiatives in accordance with the 2011 Strategic Partnership Agreement, which reflects global best practices for counterterrorism collaboration.
- Secure Economic Connectivity & Geoeconomic Options
- Increase commerce and investment through projects and alternate routes that avoid antagonistic transportation and seek resource-sector alliances with well-defined protections.
- For example, the reinstatement of the India-Afghanistan Air Freight Corridor (2025), economic engagement through the usage of Chabahar Port, and targeted investments (like Hajigak via AFISCO) with contractual and security guarantees provide India leverage and reciprocal incentives for stability.
- Advocacy for Social, Gender, and Human Rights Concerns
- India has continuously promoted women’s education, minority rights, and political inclusivity through diplomatic channels and international platforms, albeit with a pragmatic approach.
- Although it was controversial, the barring of female journalists from the Taliban’s 2025 visit to India highlighted India’s difficulty striking a balance between morality and diplomacy.
- India’s approach to engagement might be similar to the EU’s cautious diplomacy with authoritarian nations, in which assistance is contingent upon reforms.
- At the same time, India should keep growing its outreach to the general Afghan population through media and communication, cultural exchanges, vocational training, and scholarships.
Conclusion
In 2025, India-Afghanistan relations reflect a careful balance between pragmatism and principle. India continues diplomatic engagement with the Taliban to protect strategic and security interests while supporting humanitarian aid and development. Despite challenges like terrorism, Pakistan’s influence, and human rights issues, India’s steady approach aims to ensure stability, connectivity, and lasting regional peace.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What are the key developments in India-Afghanistan relations in 2025?
The reopening of India’s embassy in Kabul, the visit of Afghan Foreign Minister Amir Khan Muttaqi to New Delhi, and the promotion of India’s technical mission to full-fledged embassy are just a few of the significant improvements in India-Afghanistan relations that have occurred in 2025. In their discussions, both countries have discussed commerce, security, and humanitarian cooperation.
What are the main areas of cooperation between India-Afghanistan relations in 2025?
The restoration of humanitarian aid, medical assistance, development projects including hospital construction, capacity building, and trade (almost $1 billion in bilateral trade annually) are important areas. In addition, the parties have reopened the air freight route for direct trade and formed a trade committee.
What is the outlook for India-Afghanistan relations going forward?
Even if the outlook is positive for growing commerce and collaboration, it is still dependent on Afghanistan’s ongoing security guarantees, inclusive domestic government, and the success of economic connection projects. It is anticipated that actual engagement will continue to take precedence over official diplomatic backing.
What security assurances has Afghanistan given India?
The Taliban government has promised that terrorist attacks against India or other nations will not take place on Afghan territory. Both countries have committed to working together to combat terrorism in all its manifestations and to bolster intelligence-sharing protocols.
Sources:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Afghanistan%E2%80%93India_relations#:~:text=On%209%20October%202025%2C%20Afghan,technical%20mission%20to%20embassy%20status.
- https://www.mea.gov.in/bilateral-documents.htm?dtl/40193/India__Afghanistan_Joint_Statement_October_10_2025
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/afghan-foreign-minister-visits-darul-uloom-deoband-islamic-seminary-says-hopeful-of-stronger-ties-with-india/article70151706.ece
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/india-approach-taliban-recognition-afghanistan-muttaqi-10305973/
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/future-of-india-afghanistan-relations-is-very-bright-afghan-foreign-minister-amir-khan-muttaqi/articleshow/124473463.cms?from=mdr
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-to-upgrade-its-kabul-mission-to-full-embassy-status-jaishankar/article70147326.ece
- https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c8exzzz5dp5o
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-unveils-new-development-push-for-afghanistan-upgrades-mission-in-kabul-101760084324822.html
Leave a Reply