NEET Exam Controversy 2024
Introduction
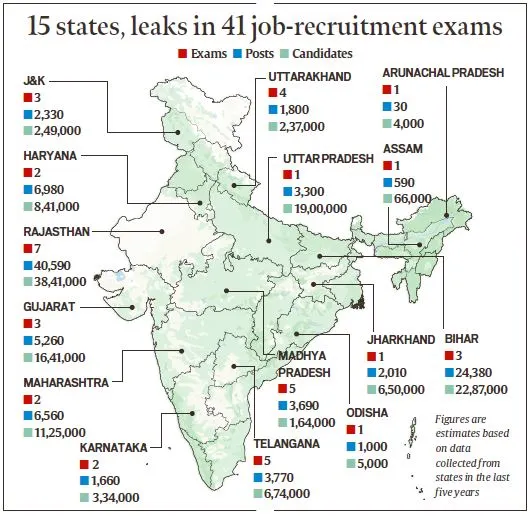
The NEET Exam Controversy has brought attention to the pervasive problem of paper leaks, an infraction that has long existed in India. There have been 70 verified exam leaks in 15 states during the last seven years, raising severe concerns about the validity of the country’s testing system.
These revelations have thrown off the schedules of 1.7 crore candidates. The recent NEET-UG 2024 paper leak, which impacted an exam taken by over 24 lakh candidates nationwide, highlights the paper leak mob’s significant impact on India’s testing system.
Why is the NEET Exam Controversy?
- Allegations of Misconduct
- On May 5, more than 24 lakh students took the NEET-UG test this year at 4,750 centers spread across 571 cities, including 14 overseas sites.
- When the results were announced on June 4, candidates raised a lot of ire right away. They claimed that over 1,500 students had received grace marks, that a disproportionately large number of students had received perfect scores, and that there had been question paper leaks.
- A bigger number of pupils than in prior years—67 students—achieved a total score of 720, according to the data. Two students received all A’s in 2023, compared to three in 2022, two in 2021, and one in 2020.
- Six of the highest scorers allegedly took the exam in the same Haryana location.
- The NTA’s Position
- The number of understudies who took the test in 2024 surpassed that of 2023 by around 3 lakh, concurring to NTA, and “the increment in candidates driven to an increment in tall scorers due to a bigger pool of candidates.”
- The NTA representative added that the 2024 NEET was “comparatively easier” than earlier exams.
- The argument was that 716 was the greatest conceivable score following the maximum of 720, and thus 718 and 719 were illogical. Six of the top applicants, according to the NTA, received “compensatory marks for loss of time.”
- The Supreme Court’s Decision
- The Supreme Court has been informed by the Center that 1,563 candidates who received grace marks in the NEET-UG 2024 would take another exam. The reassessment took place on June 23.
- The admissions counseling process will continue, according to the Supreme Court’s decision. The results will be based on the 1,563 applicants’ prior scores without the grace marks if any of them choose not to take the retest.
- Position of the Government
- The National Testing Agency “failed institutionally,” according to the Union Education Minister, when it came to the purported anomalies in the most recent National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test (NEET).
- The National Testing Agency (NTA) is conducting examinations to determine fair conduct and operational efficiency. A high-level committee led by Dr. K Radhakrishnan, the former chairman of ISRO, was announced by the Central Government.
- The report from the seven-member group is due in two months.
- After rejecting the NTA chief, the Union government set him under “obligatory hold up” at the Division of Workforce and Preparing.
- Following the finding of evidence of a paper leak by investigators in Bihar, the CBI assumed control of the NEET UG probe.
- Notification of the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024’s regulations has been given.
What is the National Eligibility Entrance Test (NEET)?
- One of the most difficult medical admission exams given in India is NEET.
- Each year, the National Testing Office (NTA) regulates the National Qualification and Entrance Test (NEET) for candidates for undergrad (MBBS, BDS, and Ayush courses).
- For admission to medical, dentistry, AYUSH, BVSc (Bachelor of Veterinary Science), and AH (Animal Husbandry) institutes in India, the single national-level undergraduate medical entrance test, NEET, is administered annually.
- Eleven languages are available for the online NEET exam: English, Hindi, Marathi, Odia, Tamil, Urdu, Bengali, Telugu, Kannada, and Assamese.
- The Central Board of Secondary Education administered the exam before the NTA (CBSE).
What is the National Testing Agency (NTA)?
- In 2017, the Indian Societies Registration Act, of 1860, was used to register the National Testing Agency (NTA) as a society.
- It is a testing organization that operates independently and sustainably and administers entrance exams for admission to postsecondary schools.
- Three top undergraduate admissions entrance tests are administered by NTA: CUET-UG for admission to several different undergraduate degrees, NEET-UG for medical, and JEE-Main for engineering admissions.
- In addition to these, the testing organization administers UGC-NET, CSIR UGC-NET, and CUET-PG for postgraduate admissions.
- NTA also administers entrance exams for Delhi University, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Common Management Admission Test (CMAT), Hotel Management Joint Entrance Examination, Graduate Pharmacy Aptitude Test, and other institutions.
Who Governance National Testing Agency (NTA)?
- The Ministry of Education appoints a distinguished educationist to chair the NTA.
- The Chief Official Officer of NTA is the Chief Common, who has the same position and compensation as the Joint Secretary of the Government of India.
- Regarding its policies, the Government of India issues directives to the NTA and the General Body, which the NTA is required to follow.
- The Governing Body, which is made up of representatives from user institutions, has been given responsibility for managing the NTA.
How National Testing Agency (NTA) Function?
- To find partner institutions from the current school system and higher education establishments that have the necessary infrastructure to administer online exams without interfering with their regular academic schedule.
- To use contemporary methods to construct a question bank covering every subject.
- To build a solid R&D culture and a team of specialists in many testing-related fields.
- To work along with global institutions such as Educational Testing Services (ETS).
- To carry out any additional investigation that the Ministries, Departments, and State Governments of the Government of India assign it.
How Far Does the Public Examinations Act, 2024 Deal with Cheating in India?
Arguments in Favour
- Computer Based Test (CBT)
- The whole scope of computer-based tests is outlined in the Rules (CBT).
- It includes everything from candidate registration, center assignment, and admit card issuance to question paper distribution and opening, answer assessment, and final recommendations.
- National Recruitment Agency’s Role
- The National Recruitment Agency of the federal government will draft the rules, standards, and norms for CBTs after consulting with relevant parties. The Center will notify those who have finalized these rules.
- Physical and digital infrastructure, standard operating procedures, candidate check-in, biometric registration, security, invigilation, and post-examination activities are all considered norms.
- Centre Coordinator
- Appointed by PSUs, public sector banks, colleges, or other government agencies, or by the federal or state governments.
- The Center Coordinator will operate as the public examination authority’s representative in coordinating the efforts of the different service providers and the examination authority, as well as in ensuring that all exam-related norms, standards, and guidelines are followed.
- Defining Public Examination Authorities
- “Any examination conducted by the public examination authority” specified in the Act’s Schedule is defined as a “public examination” under Section 2(k) of The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024.
- The UPSC, SSC, RRBs, IBPS, NTA, and other Central Government services and offices are included as open examination specialists in the Plan.
- Use of Unfair Means
- The Act’s Section 3 enumerates fifteen acts that constitute unfair testing practices in public settings “for monetary or wrongful gain.”
- It involves giving out illegal answers, leaking question papers, and tampering with answer sheets.
- Non-Bailable Provision in New Anti-Cheating Law
- To prevent cheating, the Act stipulates that offenders who commit organized crimes of cheating shall be sentenced to a minimum of three to five years in jail and a minimum fine of one crore rupees.
Arguments Against the Law
- Existing Anti-Cheating Laws
- Critics contend that since identical offenses are already penalized by law, a harsh penalty by itself won’t stop cheating.
- Despite the existence of anti-cheating legislation in certain states, cheating continues, suggesting that these laws are ineffective.
- Prevalence of Organized Cheating
- Politically connected organized crime groups frequently assist in cheating, making enforcement more difficult.
- High-profile arrests and creative cheating techniques draw attention to the continuous difficulty.
- Focus on Punitive Measures
- Some opponents argue that the emphasis on harsh punishments for exam cheaters may obscure the need for structural changes to the curriculum, assessment procedures, and student support networks.
- Declining Public Confidence
- Declining public trust in the dependability and fairness of exams has resulted in lawsuits, demonstrations, and calls for reforms from a variety of parties.
- Exam results-related disputes and demonstrations, like those involving the railway recruiting test, highlight persistent problems with the examination system that need to be properly addressed.
- Discretion of State Governments
- The legislation is meant to be a model for other states to follow, but because it leaves room for discretion, state governments may execute it differently in each state.
What Steps Should Be Taken for a Fair Examination System in India?
- Creation of a National Examination Integrity Council (NEIC)
- To guarantee consistent standards and procedures for all major exams conducted nationwide, the government should consider establishing a National Examination Integrity Council.
- The Council may carry out routine audits to evaluate the efficiency of the examination procedures and pinpoint areas that require enhancement.
- Robust governance needs to be embodied in comprehensive and error-free Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and their adherence.
- Transparent Recruitment and Accountability
- To lessen the likelihood of corruption and collusion, ensure important posts within examination bodies are filled based on merit and honesty.
- Establish strong processes for protecting whistleblowers so that they may report wrongdoing without fear of reprisals.
- On-Demand Testing
- Change to an exam-scheduling computer-based on-demand paradigm like the GRE, where students may take the test whenever it suits them. This lessens the possibility of leakage and the logistical strain of administering tests to millions of people in a single day.
- Create a sizable question pool for every subject so that the system can create distinct test questions for every applicant, reducing the likelihood of cheating
- Digital Security Measures
- Use blockchain technology to establish an unchangeable record of the test procedures, from putting up the question paper to announcing the results. This would guarantee that any manipulation is quickly identified.
- Protect candidate data and question papers from unwanted access by using cutting-edge encryption methods.
- Rigorous Enforcement
- Lower the invigilator-to-student ratio to improve oversight during assessments.
- Strict enforcement of the Public Examination Act, 2024 is necessary, and violators should face harsh consequences for malpractice, such as fines, jail time, and lifelong bans from taking tests in the future.
- Secure Transportation and Storage
- When transporting physical examination items, make use of GPS monitoring and tamper-evident packaging. Storage facilities must be extremely safe and under constant observation.
- Install CCTV cameras in every exam center to guarantee thorough coverage of every activity. In the event of any disagreements or claims of malpractice, recorded video should be examined.
- Post-Examination Processes
- Use double-blind evaluation procedures in which the response scripts are graded separately by many examiners. This lessens mistakes and prejudice.
- Create a special unit to handle complaints or inconsistencies about test findings quickly.
- Reducing Exam Pressure
- By including project work, interviews, and continual assessment in the evaluation process, you may lessen the dependency on one-day tests.
- The goal of NEP 2020 is to replace the summative, rote memorization-focused learning evaluations with a more frequent, formative, competency-based system that assesses higher-order abilities including analysis, critical thinking, and conceptual clarity.
- Cultural and Educational Shifts
- To emphasize the value of being honest in exams, hold ethics and integrity workshops and seminars for students, teachers, and exam authorities.
- Start awareness programs that emphasize the consequences of exam malpractice and encourage diligence and fairness in society.
Conclusion
We can preserve the integrity of exams by cultivating a culture of integrity at all levels—using improved oversight, strong governance structures, and extensive stakeholder involvement. In addition to safeguarding the hopes of millions of students, this vision fortifies India’s educational system and opens the door to a society that is more merit-based and egalitarian.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the NEET issue in 2024?
Amid the NEET-UG 2024 test, there was contention approximately the beauty marks given to candidates at six centers to make up for missed time. Later, the Center provided 1,563 impacted students the chance to retake the test and notified the Supreme Court that these grace marks would be eliminated.
What is the NEET Exam scandal?
There is an ongoing inquiry into the purported leak of NEET-UG documents from a Hazaribagh center, including the superintendent, center observer, and school principal. A courier company’s franchisee in Hazaribagh is also under investigation.
What is the NEET exam controversy?
The NEET Exam scandal has brought attention to the pervasive problem of paper leaks, an infraction that has long existed in India. There have been 70 verified exam leaks in 15 states during the last seven years, raising severe concerns about the validity of the country’s testing system.
Is physics removed from NEET Exam 2024?
The most recent revision to the NEET 2024 syllabus includes the deletion, inclusion, and alteration of some chapters and subjects related to biology, chemistry, and physics. Subjects from Classes 11 and 12 will be included in the NEET syllabus for 2024, with a concentration on biology, chemistry, and physics.
Sources:
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/how-a-25-minute-sbi-canara-bank-confusion-in-haryana-led-to-a-neet-controversy-affecting-24-lakh-students/articleshow/111037537.cms?from=mdr
- https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/explained-what-is-neet-ug-result-2024-controversy-why-are-students-protesting-101718259700450.html
- https://www.thehindu.com/education/neet-ug-results-2024-allegations-controversy/article68286624.ece
- https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/news/story/neet-exam-controversy-aspiring-doctors-demand-justice-over-alleged-exam-flaws-2553008-2024-06-14
- https://www.ndtv.com/education/neet-result-2024-controversy-national-testing-agency-refutes-claims-of-torn-answer-sheets-5864395
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/education/news/controversy-surrounds-neet-ug-2024-supreme-court-seeks-answers-counselling-to-proceed/articleshow/110896517.cms
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2024/Jun/06/neet-ug-result-controversy-nta-says-it-gave-marks-on-the-loss-of-time-revision-in-answer-key

Leave a Reply