The Fall of the Indian Rupee in 2025
Introduction
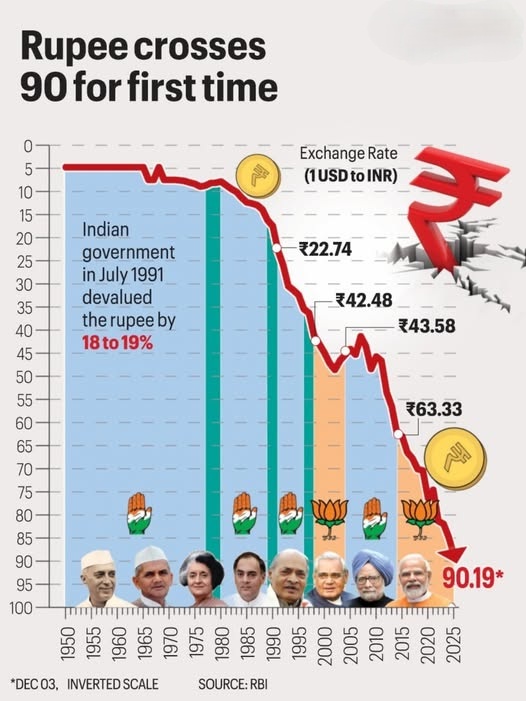
The Indian Rupee (INR) saw one of its biggest drops in contemporary history in 2025, when it first surpassed ₹90 per US dollar. This symbolic breakthrough signified a more profound change in India’s economic story than just a numerical achievement. The rupee’s fall sparked worries about inflation, household spending, and India’s competitiveness in the global market despite the country’s robust GDP growth of over 8% Businessworld.
What is the Historical Context of the Rupee?
- One USD was worth less than ₹4 in 1947, the year of independence.
- Inflation, reliance on oil imports, and chronic trade deficits all contributed to the currency’s gradual decline over the decades.
- The rupee fluctuated between ₹83 and ₹85 per dollar by 2024 before sharply declining in 2025.
What are the Causes of the falling Indian Rupee?
- Sustained FPI Outflows
- Since January 2025, foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) have transferred money to markets that offer higher yields, withdrawing about Rs 1.48 lakh crore.
- The demand for the US dollar as a safe-haven asset has also surged due to global geopolitical uncertainties.
- US–India Trade Deal Uncertainty
- The uncertainty surrounding future tariffs and export competitiveness brought forth by the trade agreement’s delays has eroded trust in India’s external sector and increased pressure on the currency.
- Trade Deficit and Current Account Imbalance
- India imports a lot more goods than it exports, especially machinery, electronics, and crude oil.
- The current account deficit grew in 2025 as a result of rising oil prices, which raised demand for dollars.
- In October 2025, imports increased by 16.6% while merchandise exports decreased by 11.8%.
- The rupee is under more strain now that the trade gap has grown due to declining exports and dramatically increasing imports.
- Increased Brent crude prices increase India’s import bill, exacerbating the country’s trade deficit and devaluing the rupee.
- High Gold Imports
- In October 2025, imports of gold increased by around 200%. Although rising prices increased the value of gold stockpiles, they were insufficient to offset overall losses, and domestic high gold prices made the import bill much worse.
- The current account deficit has grown as a result of these increased gold imports, which have also increased the pressure on the rupee’s depreciation.
- Capital Outflows
- Due to increased US interest rates and worldwide uncertainties, foreign investors withdrew their funds from Indian markets.
- Dollar inflows decreased as both foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investment (FPI) slowed.
- RBI’s Policy Approach
- Instead of vigorously protecting the rupee, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) adopted a moderate intervention strategy, letting it decline.
- This sped up depreciation but prevented depletion of foreign reserves.
What are the Consequences of a falling Indian Rupee?
- Impact on Households
- The cost of transportation and power increased due to the dramatic increase in fuel prices.
- Indian students’ living expenses and tuition fees increased as the cost of education overseas increased.
- Due to rising travel expenses, many people can no longer afford to take vacations abroad.
- Inflationary Pressures
- The cost of imported products increased, including gadgets and medications.
- The danger of inflation rose, reducing household purchasing power and increasing EMIs.
- Corporate Challenges
- Businesses that relied on imported raw materials and machines had to pay more.
- Exporters saw a slight increase, but the slowdown in global demand outweighed the gains.
- Macroeconomic Stability
- The decline of the rupee hampered monetary policy, requiring the RBI to strike a balance between growth and inflation management.
- Due to rising dollar repayment costs, India’s external debt servicing expenses increased.
How can the Indian Rupee be strengthened?
- Expand Rupee-Based Trade Settlement
- Expand Special Vostro Rupee Accounts (SVRAs) with additional nations to lessen reliance on the dollar.
- Encourage agreements for Local Currency Settlement (LCS), particularly with important trading partners in the Gulf, Asia, and Africa.
- Reduce the need for USD in trade by increasing bilateral Memorandums of Understanding for INR-based invoicing and payment.
- Deepen the Global Market for INR
- Create a worldwide INR forex market so that foreign banks can conduct 24/7 Rupee transactions.
- Encourage the inclusion of Indian G-secs in the main international bond indices to draw in long-term passive foreign investment.
- Simplify onboarding, paperwork, and KYC requirements for global custodians and FPIs. Expand the use of the Rupee offshore by allowing Indian banks to lend to non-residents in INR. Encourage the use of Masala Bonds to raise INR worldwide.
- Strengthen External Sector Stability
- Increase currency swap arrangements to ensure liquidity support during periods of volatility.
- Maintain substantial foreign exchange reserves and adjust the RBI’s involvement to prevent chaotic fluctuations.
- Instead of depending solely on depreciation, use structural improvements to increase export competitiveness.
- Boost Global Acceptance of INR
- Continue expanding UPI internationally so that Rupee-linked digital payments are widely available.
- Increase the Rupee’s legitimacy as a reserve currency by positioning it for inclusion in the International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) Special Drawing Rights basket.
- Domestic Reforms to Support a Strong Rupee
- Increase high-value manufacturing and diversify export markets to lower the trade imbalance.
- Use measures like digital gold options and gold monetisation to reduce gold imports. To draw consistent capital flows, maintain a responsible fiscal policy and stable inflation.
Conclusion
The fall of the Indian Rupee in 2025 is a reminder that currency strength is shaped by global forces as much as domestic performance. While India’s economy remains resilient, external shocks, trade imbalances, and capital outflows expose vulnerabilities. For households, the depreciation means higher living costs. For policymakers, it underscores the need for structural reforms in trade, energy, and investment. And for businesses, it is a call to innovate and localise supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What caused the rupee’s value to drop to an all-time low?
Strong demand for the US dollar as a safe-haven asset worldwide, substantial FPI outflows, and uncertainty around the India-US trade agreement all contributed to the decline.
What strategy is India employing to lessen its reliance on the US dollar in commerce?
Special Vostro Rupee Accounts (SVRAs) and Local Currency Settlement agreements are being expanded in India to enable invoicing and payments based on Indian rupees.
How may the rupee benefit from the inclusion of Indian G-secs in international bond indices?
It increases foreign exchange liquidity and supports rupee stability by bringing consistent passive investment flows from international funds.
What is the main distinction between depreciation and devaluation that applies to India?
India uses a floating/managed float exchange-rate system rather than a fixed one, which causes depreciation—a market-driven decline in the value of the rupee.
Sources:
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/rs-90-to-a-dollar-whats-driving-the-fall-and-why-it-matters-to-you-explained/articleshow/125734691.cms
- https://www.reuters.com/world/india/indian-rupee-falls-90usd-persistent-outflows-trade-deal-limbo-2025-12-03/
- https://www.indiatoday.in/business/story/indian-economy-gdp-growing-why-is-rupee-falling-currency-crisis-explained-2830631-2025-12-04
- https://www.thehindu.com/data/rupee-hits-record-low-of-90-calculated-move-by-rbi-or-a-sign-of-losing-control/article70365760.ece
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/markets/forex/the-way-its-going-will-rupee-breach-the-100-mark-sooner-or-later/articleshow/125757713.cms?from=mdr
- https://www.cnbc.com/2025/12/05/india-cuts-rates-to-as-expected-as-central-bank-rbi-warns-of-further-reductions.html
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2025-11-27/inr-usd-why-is-india-rupee-so-weak-what-does-it-mean-for-prices-incomes
Leave a Reply