
Introduction
Freedom of Press is essential for preserving democracy and promoting an open, responsible government. However, recent measures, such as searches, seizures, and arrests of journalists connected to the web portal NewsClick, have heightened worries about the security of digital data and press freedom in India. India is dealing with a challenge from digital authoritarianism in the age of the digital revolution. In order to protect journalistic freedom in India at this crucial time, the nation requires both political action and judicial determination.
What is Freedom of Press?
A key value, press freedom, permits journalists and media outlets to work free from censorship or outside influence from the government. It is fundamental to the exercise of one’s right to free speech and is necessary for a democratic society.
The following essential elements are all part of freedom of press:
- Freedom from Censorship: Without governmental censorship, journalists and media organizations should be permitted to print or broadcast news and information.
- Access to Information: A free press must have access to data and sources in order to research and cover topics of public interest.
- Independence: Editorial independence guarantees that news reporting is fact-based and free from outside influence.
- Protection of Sources: To encourage informants and whistleblowers to come forward with information without concern about exposure or retaliation, journalists should be allowed to safeguard their sources.
- Pluralism and Diversity: A varied array of ideas and opinions should be represented by a free press in order to promote open discourse and discussion in society.
- Accountability: By inquiring into and covering the activities and choices of people in authority, the media should hold them responsible.
What is Constitutional Background of Freedom of Press?
The Constitution makes no provision relating to press freedom. However, freedom of the press or the media refers to the rights enumerated in Article 19(1)(a) of the Indian Constitution, which also guarantees freedom of speech. Allowing citizens to express their thoughts in favor of or against the activities of the government, stimulates independent media and advances democracy.
- Everyone has the right to freedom of speech, which is stated in Article 19 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. This right includes the freedom to hold opinions without interference and the ability to seek, receive, and share information and ideas across all media and geographic boundaries.
- However, in order to safeguard the country and its integrity, Article 19(2) has a number of limitations.
What is the Status of Freedom of Press?
- According to the degree of freedom provided to journalists, the World Press Freedom Index ranks various nations and geographic areas.
- Since 2002, it has been released annually by Reporters Without Borders.
- Five contextual indicators—political context, legal system, economic environment, sociocultural context, and safety—are used to assess any nation or territory’s score.
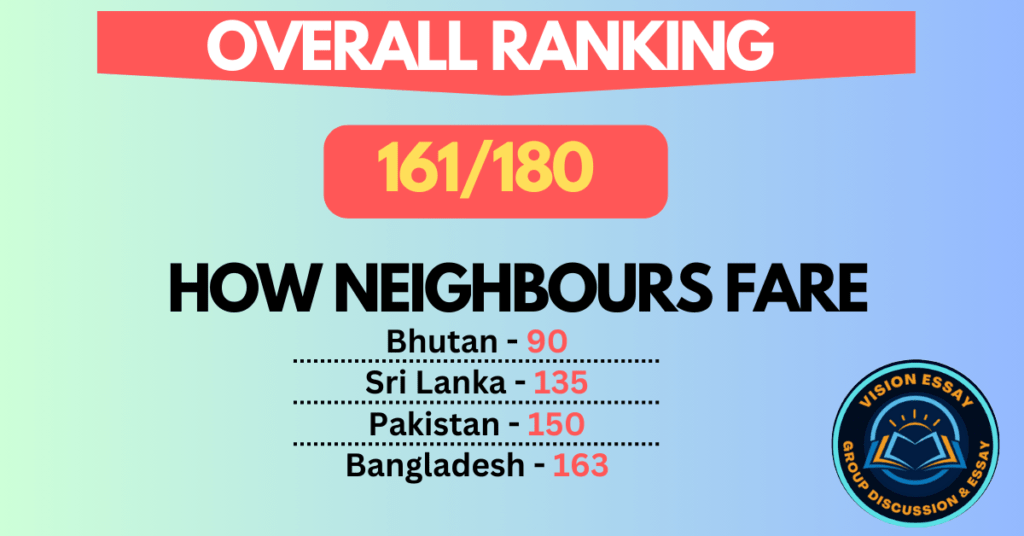
- India received a score of 36.62 out of 100 in 2023, placing it 161st out of 180 nations. India was ranked 150 in 2022.
What is the Importance of Freedom of Press?
- Democracy and Accountability: Investigating and reporting on government choices, policies, and acts, journalists hold politicians responsible for their deeds.
- Information Dissemination: In order to make educated judgments and actively engage in the democratic process, it aids individuals in staying updated about current affairs, governmental actions, and social concerns.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in governmental operations and decision-making processes is encouraged by a free press. It aids in exposing covert plans, conflicts of interest, and other elements that could affect how the government acts.
- Diverse Voices: India is a multicultural nation with many different languages, customs, and viewpoints. A free press ensures that the issues of many groups are heard by providing a forum for varied voices and opinions.
- Protection of Fundamental Rights: A free press protects essential rights, such as the freedom of speech and access to information. By defending the rights of people and groups, it contributes to the protection of these rights.
- International Standing: India’s dedication to press freedom has an impact on its standing internationally. Maintaining press freedom shows a dedication to democratic principles and human rights, which improves India’s reputation abroad.
Also read: India US Relations 2023
What are the Challenges faced with Freedom of Press in India?
- Government Interference: Government meddling with media outlets’ editorial independence has happened on occasion. Budgets for advertising may be used by governments as a mechanism to reward or penalize media companies, which can have an impact on their reporting.
- Legal and Regulatory Constraints: Defamation, sedition, and national security legislation are only a few examples of the laws in India that can be used to limit journalistic freedom. These restrictions have occasionally been used to intimidate media outlets and journalists.
- Threats and Violence: In India, journalists frequently experience physical threats and violence, particularly when covering touchy subjects like corruption, organized crime, or inter-communal strife. In the course of their work, several journalists have been harmed or even killed.
- Ownership and Control: In India, ownership of the media is frequently concentrated in the hands of a small number of influential parties, which can have an impact on editorial choices and reduce the diversity of viewpoints in the media environment.
- Defamation Lawsuits: Defamation lawsuits are routinely filed against journalists and media outlets in India, which may be time- and money-consuming.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Ensure a Freedom of Press in India?
- Promote Transparency
- Enact stringent open-government and access-to-information rules to encourage openness and give journalists access to public data.
- Encourage media ownership transparency to avoid media consolidation and conflict of interest.
- Strengthen Legal Protections
- Reform legislation like sedition and defamation laws can be used to impede journalistic freedom.
- Ensure prompt and impartial legal proceedings in incidents involving abuses of press freedom.
- Public Broadcasting Independence
- Ensure that public broadcasting organizations are free from governmental interference and control.
- Establish boards of public broadcasters that are competent and objective, and make sure their financing is reliable and unbiased.
- Promote Journalistic Ethics
- Encourage media companies to abide by a code of ethics that prioritizes truthfulness, justice, and impartial reporting.
- Encourage journalists to pursue professional growth and training to uphold the highest ethical standards.
- Educate the people on the value of an unbiased, free press in a democratic society.
- International Cooperation
- To advance press freedom and exchange best practices, work with international bodies like UNESCO and other press freedom organizations.
- A free and secure environment for journalists and media professionals is the goal of the UN Plan of Action on the Safety of Journalists.
Conclusion
It will need a coordinated effort from many stakeholders with a common dedication to safeguarding the values of a free press in a democratic society to address the issue of press freedom in India. To guarantee a thriving and autonomous media ecosystem in the nation, a complicated task demands constant attention and effort.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the current situation of freedom of press in India?
According to the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index, India’s position in terms of press freedom dropped from 150 in 2022 to 161 in 2023, out of 180 nations, with the organization claiming that the situation for journalists was “very serious” in the nation.
What is Article 19 1 A freedom of press?
All people have the right to freedom of speech and expression, as stated in Article 19(1)(a). This suggests that everyone has the freedom to share their thoughts and ideas. This covers not just verbal communication but also literature, visual media, motion pictures, advertisements, etc.
What is the scope of freedom of press?
Article 19’s core claim is as follows: “Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression, including the freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive, and spread information and ideas through any media and without regard to boundaries.”
What is the role of press in freedom struggle of India?
The press had a crucial role in the fight for freedom because it made it easier for the general public to understand the harsh policies of the colonial authority, which led to the ignition of numerous revolutionary activities.
Sources:
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-slips-in-world-press-freedom-index-ranks-161-out-of-180-countries/article66806608.ece
- https://indianexpress.com/article/india/india-slips-11-positions-world-press-freedom-index-8589968/
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/education/news/world-press-freedom-day-2023-history-theme-and-significance/articleshow/99948107.cms
