Hepatitis B: A Health Concern For India
Introduction
According to new research by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital in New Delhi, there is a lack of public awareness and information in India about Hepatitis B, a potentially deadly illness that may cause cancer and liver cirrhosis.
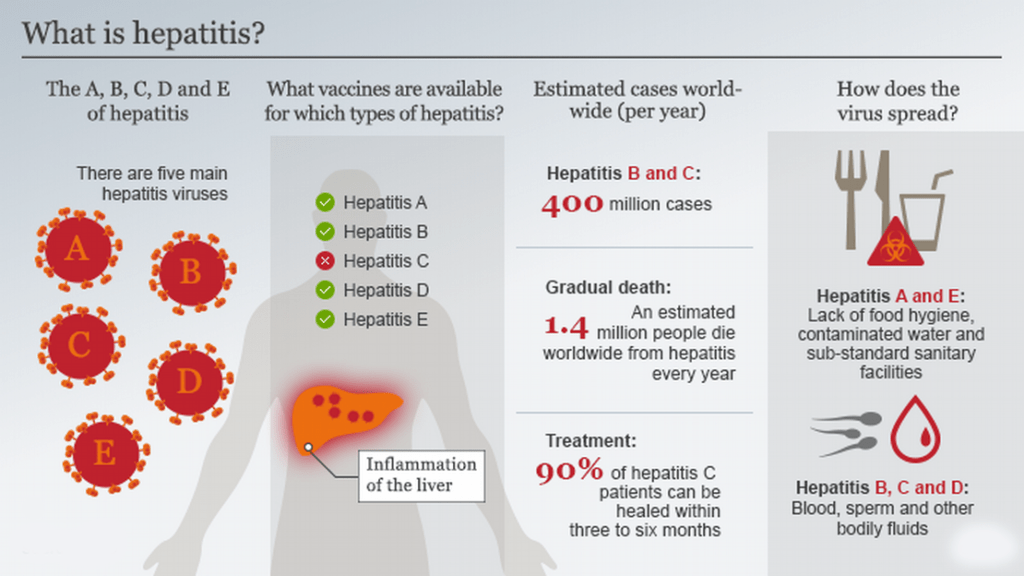
What is Hepatitis?
- Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease of the liver that is characterized by irritation or enlargement of the liver cells for a variety of reasons.
- Acute liver inflammation is typified by symptoms such as fever, jaundice, and vomiting, whereas chronic liver inflammation lasts more than six months without any noticeable symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis?
- Fatigue: Feeling exhausted even after adequate rest.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort: Pain or tenderness in the area of the liver, which is located in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting: Feeling sick to your stomach and possibly vomiting.
- Loss of appetite: Not feeling hungry or having a reduced desire to eat.
- Dark urine: Urine may appear darker than usual, often described as tea-colored.
- Pale-colored stools: Stools may become lighter in color than usual.
- Joint pain: Some people with hepatitis may experience joint pain or discomfort.
- Fever: Mild to moderate fever is common, especially in acute cases.
- Muscle aches: Generalized muscle pain or discomfort.
- Itchy skin: Some individuals with hepatitis may experience itching.
- Flu-like symptoms: Symptoms such as headache, fever, and general malaise may occur, particularly in acute cases.
What are the Causes of Hepatitis?
- Hepatotropic viruses, such as A, B, C, D, and E, are usually the cause of hepatitis, while other viruses, such as the varicella virus, can also cause the illness.
- The Covid-19 virus, SARS-CoV-2, may also harm the liver.
- Some of the other causes include abuse of drugs and alcohol, fatty liver hepatitis, or autoimmune hepatitis, in which the body produces antibodies directed against the liver.
Also read: Urinary Tract Infection(UTI), Symptoms and Its Cause 2023
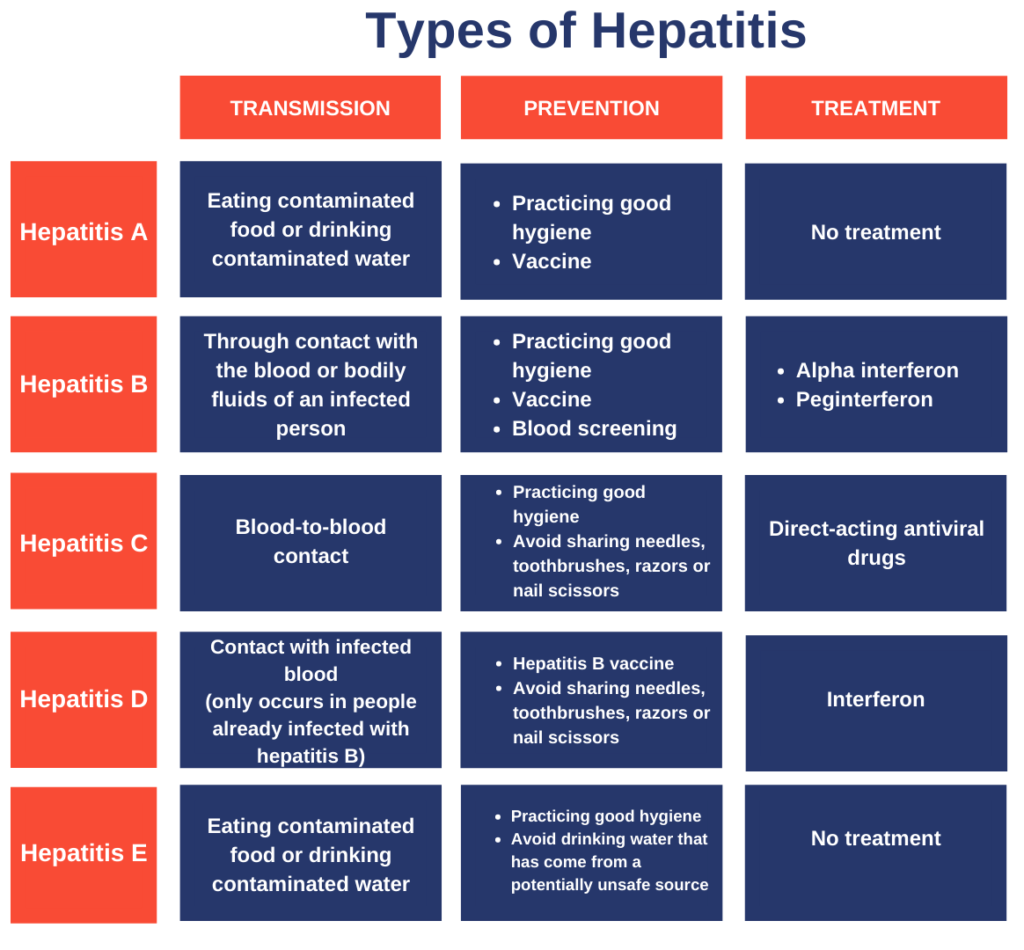
What are the types of Hepatitis?
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV)
- Hepatitis A is a liver infection that can range in severity from moderate to severe. It is spread via tainted food or water, direct contact with an infected individual, and vaccination. The majority of people who get the vaccine recover completely and get lifetime immunity.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- Vaccination can prevent hepatitis B, a viral infection that can cause acute or chronic liver disease and is commonly passed from mother to child through early childhood contact, intercourse, or improper injections.
- Vaccinations against hepatitis B are quite effective at preventing HBV infection if given before HBV exposure.
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
- Hepatitis C is a bloodborne virus that is mostly spread by improper healthcare practices, blood transfusions, injectable drug use, and sexual activities. It can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, with severity ranging from moderate to serious, including liver cirrhosis and cancer.
- With direct-acting antiviral medications (DAAs), cure rates surpass 95%; nevertheless, there is no reliable vaccination and restricted access to diagnosis and treatment.
- Hepatitis D virus (HDV)
- About 5% of people with chronic HBV infection worldwide are infected with hepatitis D, a virus that requires hepatitis B virus (HBV) to replicate. Co-infection or super-infection is more common in drug users, dialysis patients, and indigenous populations. This poses a serious risk to liver health, including the possibility of cancer or death.
- Hepatitis B vaccination can help prevent it, while treatment effectiveness is still rather low.
- Hepatitis E virus (HEV)
- Hepatitis E, which is caused by HEV infection, is quite common worldwide, especially in East and South Asia. It is spread by polluted water, and while there is already a vaccine approved in China and a few other countries, research is still being done to find more vaccinations internationally.
What are the Government Initiatives to Tackle Hepatitis?
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program: By 2030, the program hopes to eradicate viral hepatitis as a risk to public health in the nation.
- India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP): Hepatitis B, tuberculosis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, pneumonia, meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), measles, rubella, Japanese encephalitis (JE), and rotavirus diarrhea are among the eleven vaccine-preventable diseases that are covered by the UIP.
What are the Global to Tackle Hepatitis?
- WHO’s global hepatitis strategy
- Coalition for Global Hepatitis Elimination (CGHE)
- Global Hepatitis Programme
Conclusion
Hepatitis B presents a significant health concern in India due to low public awareness. With potential severe consequences like cancer and liver cirrhosis, understanding its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures is crucial. Government initiatives such as the National Viral Hepatitis Control Program and global efforts like WHO’s strategy are vital steps towards tackling this issue and achieving a hepatitis-free future.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Is hepatitis B contagious?
Yes, hepatitis B is highly contagious and can be transmitted through contact with infected blood or body fluids.
Can hepatitis B be cured?
While there is no cure for hepatitis B, treatment can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
Who is at risk of hepatitis B?
Individuals at high risk of hepatitis B include those who engage in unprotected sex, share needles or syringes or are born to infected mothers.
How can hepatitis B be prevented?
Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination, practicing safe sex, avoiding sharing needles, and ensuring proper hygiene practices.
Sources:
- https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/india/health-topic-pdf/factsheet-b-hepatitisday2016.pdf?sfvrsn=da61ef0_2#:~:text=In%20India%2C%20the%20prevalence%20of,of%20hepatitis%20B%20related%20complications.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8518333/
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1566140
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/voices/time-to-eliminate-hepatitis-b-from-india/
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/how-to/is-hepatitis-a-dangerous-here-is-everything-you-need-to-know-about-hepatitis-a/articleshow/101096836.cms?from=mdr
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis_B