Iran and Israel Conflict

Introduction
Iran used more than 300 projectiles, including more than 120 ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and almost 170 drones, to launch a massive strike on Israel. It was often believed that this move was taken in revenge for a deadly attack on Iran’s consulate in Damascus, Syria.
Beyond earlier clashes between Israel and Hamas, the incident denotes a major uptick in the continuing Iran and Israel Conflict. This incident emphasizes the possibility of more violence in the Middle East and draws attention to the growing tensions between two of the most adamant opponents in the area.
What is the Historical Background of Relations Between Iran and Israel?
- Pre-1979 Iran-Israel Ties
- One of the first nations in the area to recognize Israel upon its creation in 1948 was Iran.
- The first Arab-Israeli conflict broke out in 1948 as a result of the Arab governments’ resistance to Israel. Iran did not participate in the war, and following Israel’s victory, it forged relations with the Jewish state.
- The “periphery doctrine” was developed by Israel under its first prime minister, David Ben Gurion, to fight Arab antagonism by forging relationships with non-Arab, mostly Muslim, nations in the Middle East, according to a Brookings Institute report. This approach concentrated on establishing alliances with countries that felt alone in the area and shared a pro-Western stance, such as pre-revolutionary Iran and Turkey.
- Iran was controlled by Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi from 1941 to 1979, and he had a pro-Western foreign policy. Iran kept diplomatic links with Israel and even continued to supply oil to Israel throughout this time while suffering an economic embargo from Arab governments.
- The 1979 Revolution
- Iran became a religious state after the Islamic Revolution of 1979 toppled the Shah. Israel was now viewed by the authorities as an occupying force on Palestinian territory.
- Ayatollah Khomeini, the supreme leader of Israel in Iran, referred to the United States as the “Great Satan” and Israel as the “Little Satan,” seeing both as countries meddling in the area.
- Iran also aimed to become more powerful in the area by taking on Israel and Saudi Arabia, two of the US’s closest allies.
- A Shadow War after 1979
- Consequently, the relations between the two nations deteriorated. Although Israel and Iran have never clashed militarily, they have each tried to harm the other by using proxies and small-scale strategic strikes.
- To stop itself from developing nuclear weapons, Israel briefly targeted several institutions and nuclear experts in the early 2010s.
- It is thought that the US and Israel created the harmful computer malware Stuxnet in 2010. It was the “first publicly known cyberattack on industrial machinery” and was directed against Iran’s nuclear plant in Natanz, targeting a uranium enrichment facility.
- Meanwhile, Iran is thought to be behind the financing and backing of several anti-US and anti-Israel violent organizations in the area, including Hamas in the Gaza Strip and Hezbollah in Lebanon.
- Because of this backing, worries about a confrontation or a growing conflict have surfaced in recent months.
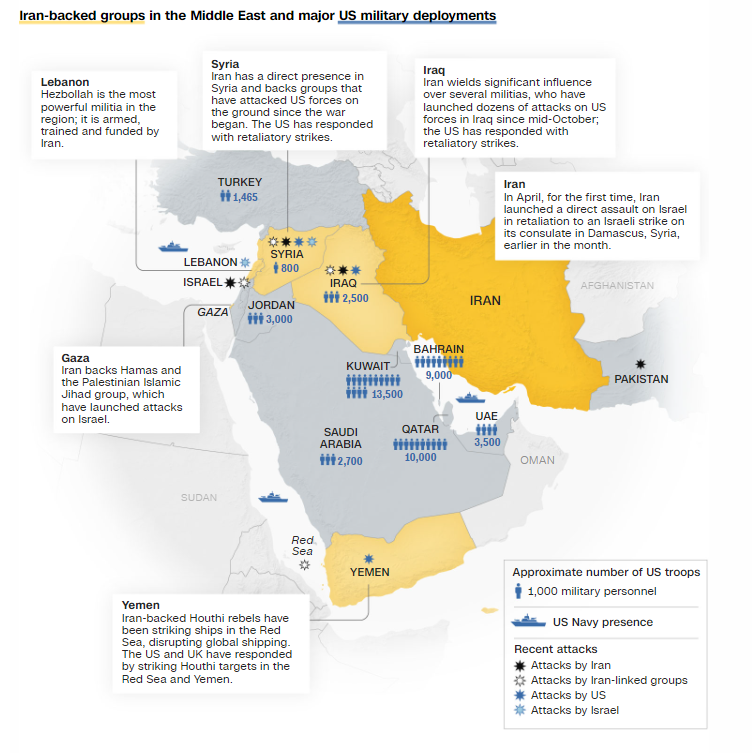
What Significant Events Set Up Iran’s Attack on Israel?
- Elimination of the United States from the Iran Nuclear Deal: In 2018, Israel celebrated President Trump’s decision to remove the United States from the nuclear agreement with Iran, referring to it as “a historic move” following years of pushing against it.
- Iran’s Army General assassinated: Israel rejoices in 2020 after an American drone attack in Baghdad results in the death of General Qassem Soleimani, the head of Iran’s Revolutionary Guards’ foreign branch. Iran retaliates by attacking US military bases in Iraq with missiles.
- Strike by Hamas Missiles: The terrorist organization sponsored by Iran, Hamas, launched a missile strike on Israel in October of 2023. Israel attacked Gaza with airstrikes in retaliation.
- Israel Raids and Attacks Medical Institutions: In November 2023, Israel began raiding and assaulting medical institutions since it was believed that Hamas was carrying out its warfare from these hospital structures.
- Red Sea Incident of the Houthi organization: In November 2023, the Houthi organization, which is located in Yemen and is supported by Iran, made a helicopter landing on the Galaxy Leader cargo ship while it was traveling through the Red Sea. This initiated the ‘Red Sea Crisis,’ which ultimately resulted in problems with the supply system.
- Elevation of Israel’s Ground attacks: Beginning in December 2023, Israel increased the intensity of its ground attacks in the Gaza Strip. The number of refugees and the death toll increased as a result. An “early and durable resolution” between the warring states was demanded by India.
- Two senior commanders and seven members of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard are among the seven officers who were killed in what seems to be an Israeli air strike on the Iranian embassy compound in Damascus. Israel did not admit guilt nor refute it.
- Iran’s Missile Attack on Israel: Iran attacked Israel with missiles in April of 2024. Allegedly, the incident happened in retaliation for an alleged Israeli strike on Iran’s embassy in Syria. This was the first time Iran had attacked Israel directly from its soil.
- Israel’s Multi-Layer Air Defense: According to the Israel Defense Forces (IDF), 99% of Iran’s inbound rockets were intercepted by the Israeli air defense system. Israel was also defended by the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and other Middle Eastern friends.

How the Iran and Israel Conflict May Impact the World?
- Possible Israeli Response May Increase Regional Escalation
- Retaliation cannot be completely excluded from the decision-making process, given the prevalent Israeli perception that Iran with nuclear weapons poses an existential danger to Israel.
- The possibility of regional escalation increases if diplomatic attempts to reduce tensions or find a peaceful settlement are unsuccessful and leave armed action as the only choice.
- Potential to Disrupt Oil Supplies
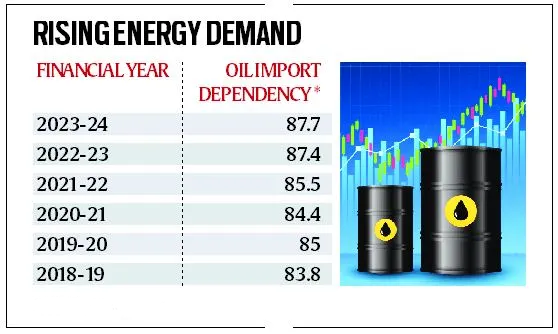
- Iran is OPEC’s (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) third-largest crude oil production. The supply of crude oil will be seriously interrupted if tensions between Israel and Iran continue to rise.
- India is the third-largest importer and user of crude oil, importing more than 80% of its requirements, therefore this will negatively impact the mood of the Indian share market.
- Spike in Inflation and Capital Outflow
- Commodity prices will rise as a result of supply interruptions if geopolitical tensions continue to rise. Due to geopolitical tensions that impact the price of commodities like copper, zinc, aluminum, nickel, and crude oil, inflation will continue to be high on a global scale.
- These worries are likely to make investors more wary, and they could decide to shift their investments from risky assets like Indian equities to safer ones like gold (bullion).
- Because of increased uncertainty and decreased business profitability, bond prices might decline, corporate borrowing costs could go up, and stock markets could decline.
- Trade and Travel Disruptions
- In addition to the impact on oil prices, the possibility of an all-out conflict between Iran and Israel might also have an impact on trade and tourism. The maritime and aviation industries could be affected.
- In actuality, the airspaces of several nations in the area, including Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, Iran, and Lebanon, were briefly blocked and eventually reopened, but with limitations.
- Analysts have predicted that the recent escalation in tensions between Iran and Israel will affect India’s exports to Europe.
- India’s Strategic Dilemma
- India has difficulties on the operational and policy fronts as a result of its long-standing strategic ties to Israel and Iran.
- India cherishes its strategic alliance with Israel, which covers information sharing, technology transfer, and defense collaboration. India and Iran do, however, still have historical and commercial links that include energy imports and infrastructure development.
- India aims to protect its interests, such as energy security and the well-being of its diaspora, by preserving stability in the Middle East.
Also read: A Dark Truth of Israel-Hamas War, 2023
What Are Some Potential Ways to Defuse the Iran and Israel Conflict?
- Sustainable Ceasefire and Two-State Solution
- Israel should obey UN resolutions to end the seventy-year conflict by achieving a two-state solution, accept a durable truce in Gaza as soon as feasible, and open its borders to international humanitarian aid.
- The only practical path forward for the region’s long-term security, peace, and stability is the two-state solution. Although all parties are aware of the difficulties and possibilities, the aim is not simple.
- Dialogue and Diplomacy
- A long-lasting truce between Israel and Iran has to be mediated by an international effort. Finding common ground and fostering trust might be achieved by encouraging both nations to hold direct discussions led by international mediators.
- Direct negotiations between Iran and Israel might be arranged by an impartial third party, such as the UN or the European Union.
- Addressing Nuclear Proliferation Concerns
- To assure compliance with the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), Iran could abide by its conditions and permit foreign inspections of its nuclear sites.
- Israel might agree to refrain from using force against Iranian nuclear facilities in exchange for acknowledging Iran’s right to peaceful nuclear energy.
- Regional Cooperation
- To solve common security issues and promote stability in the Middle East, Iran, and Israel should work together within the framework of regional organizations like the Gulf Cooperation Council and the Arab League.
- Iran and Israel could be less likely to go to war if a comprehensive regional security architecture that takes into account the worries of all parties involved in the Middle East is developed.
- Long-Term Vision for the Middle East
- Together, the regional powers might create a comprehensive security architecture for the Middle East that includes weapons control agreements, measures to foster confidence and peaceful conflict resolution procedures.
- A climate that is favorable to peace and reconciliation can be established by addressing underlying problems such as territorial conflicts, historical grudges, and religious fanaticism.
- Normalization of Relations
- Iran and Israel might follow the path of peace accords between Israel and several Arab governments, such as the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain, and work toward repairing diplomatic ties by swapping ambassadors, reopening embassies, and encouraging people-to-people interactions.
Conclusion
The Global South and Global Governance are impacted by the continued unrest in the Middle East. As such, it is imperative that the world community press all involved parties to desist from using violence and give diplomatic discussions priority to find answers. It is essential to adopt sensible and well-balanced measures to mitigate the crisis in the area and avert long-term unrest.
Why are Iran and Israel enemies?
Iran and Israel have longstanding animosity rooted in religious, ideological, and geopolitical differences. Iran opposes Israel’s existence, viewing it as an occupying force in Palestine, while Israel sees Iran as a threat due to its support for militant groups.
What is the main point of Iran and Israel Conflict?
One of the main points of contention is Iran’s nuclear program, which Israel and many Western countries fear could lead to the development of nuclear weapons.
How does the conflict between Iran and Israel affect the region?
The conflict has led to proxy wars, humanitarian crises, and economic disruptions, contributing to instability and insecurity in the Middle East.
What efforts have been made to address the conflict between Iran and Israel?
International diplomatic efforts, including negotiations and sanctions, have been employed to address the root causes of the conflict and promote peace and stability in the region.
Sources:
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-68811276
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iran%E2%80%93Israel_proxy_conflict
- https://edition.cnn.com/2024/04/14/middleeast/why-iran-attack-israel-intl/index.html
- https://www.nytimes.com/2024/04/14/world/middleeast/iran-attacks-israel-history.html
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/india-stake-iran-israel-conflict-tensions-9269260/
Leave a Reply